
w entered by the user, w is compared with the program's known set of words. If the spelling of w matches a spelling known to the program, no action is taken. Otherwise, the program alerts the user to the perceived error.

Spellcheck can be implemented rather easily with a hash table. The hash of each word w to be spellchecked is used to index into the key/value table, and the discovery of an element containing a key equal to w is interpreted to mean that the word is spelled correctly.
In some regards, this solution is pretty great. We get average-case constant-time dictionary_gets and amortized constant-time dictionary_puts. But we can do better.
Consider the following example of a trie.
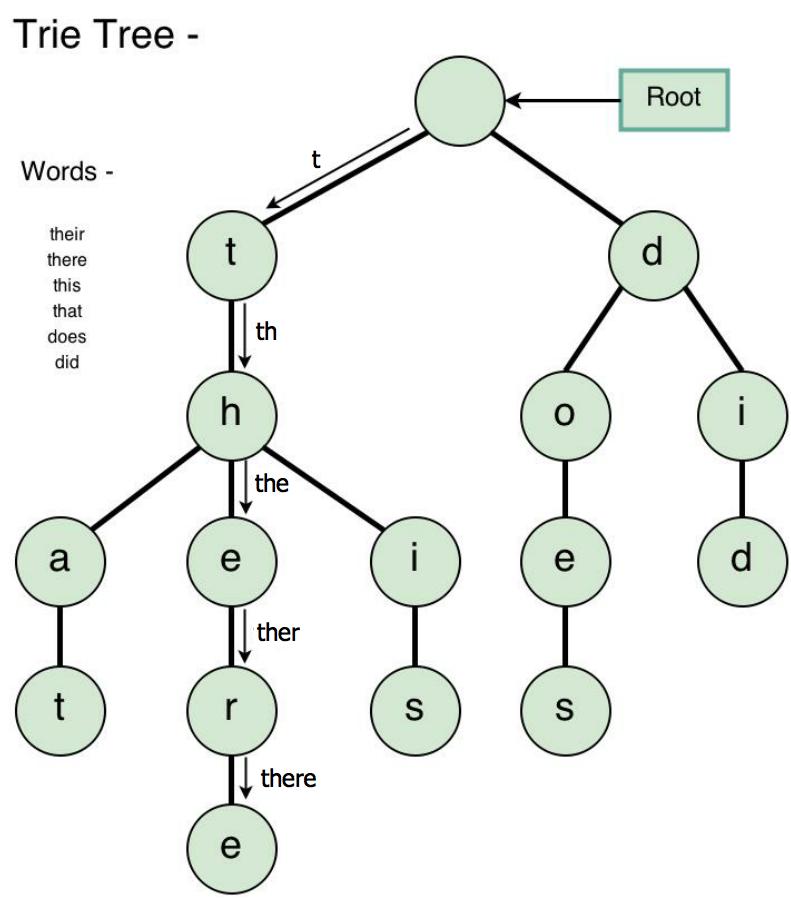
The root is a dummy element––that is, it codifies our starting state. If we walk down a trie, we can spell out a word using the contents of each element. An element that corresponds to the completion of a word is marked by setting the flag is_word to true––even though the abstraction shown above does not go into such detail.
The above scheme is also implementation-agnostic with regards to branching. In determining whether "there" is a valid spelling of a word, how do we step from the h element to the e element? There are several possible mechanisms by which this routing can be accomplished, but, for the purposes of this assignment, we'll be using a hash table. More specifically, if l gives the number of legal characters accepted by the dictionary, for each element n there exists a gmap, and for each gmap there exist between 0 and l mappings (inclusive) between a single character k as a key and a pointer to the element corresponding to k as a value.
Write a program called Spellcheck that initializes a dictionary so as to contain
all words w found in a file, checks each word w' contained in another
file against each w stored in the trie, and outputs all w' that could not
be matched to a w.
Output should be
formatted as a sequence of words delimited by newline characters (e.g.
thansk\nfreind\nmoer\n...). The flag -d is immediately followed by the name of a file
that Spellcheck is to interpret as its dictionary, and the flag -x is immediately
followed by the name of a file that Spellcheck is to use as its source of words to spellcheck. For both files,
words are expected to be non-null.
You will find that most of the work has already been done for you. You can pick up where we left off in class with the dictionary.c file located in /c/cs223/hw10/FromClass/. Note, however, that your dictionary ADT will have to conform to the interface defined in the header file /c/cs223/hw10/Required/dictionary.h.
dictionary is a typedefed struct containing
a pointer to a dummy element node, the root of the trie––as well as a size data
member to reflect the number of added words. Each element e is a
typedefed struct consisting of a pointer (children) to a gmap, a
pointer (value) to e, and a flag (is_word) to indicate whether or not
e corresponds to the completion of a word. Note: the use of value as
a self-reference enables facile traversal of the tree, as gmap_get returns the value associated
with a provided key. More specifically, an element pointer can be updated within a loop to be the result of
gmap_get until gmap_contains_key returns false.
dictionary_create should create a dictionary and initialize it to contain a dummy element as its head. It should also initialize the size data member.
dictionary_put_word should update the dictionary by traversing the trie, creating new nodes as necessary, until the last character in the given word is processed. At this point, the current element is set to be a valid word. This function returns whether or not the put was successful.
dictionary_is_word should traverse the trie until either 1) an element that has no mapping to another element containing the next character in the provided word is encountered or 2) all characters in the provided word have been checked against elements in the trie. In the former case, false is returned. In the latter case, the most-recently examined element's is_word field is returned.
dictionary_destroy destroys the dictionary supplied as an argument.
dictionary.c, your log,
and a makefile with Spellcheck set to be its default target as submission number 10. You should not submit any files found in /c/cs223/hw10/Required, and your makefile should assume these files have been copied into the current directory rather than that they are in their original locations.
[crb84@hare hw10]$ /c/cs223/bin/submit 10 dictionary.c makefile log
Copying dictionary.c
Copying makefile
Copying log
[crb84@hare hw10]$ /c/cs223/bin/testit 10 Spellcheck
/home/classes/cs223/Hwk10/test.Spellcheck
Copying char_key.cCopying char_key.hCopying dictionary.hCopying gmap.cCopying gmap.hCopying spellcheck.cExecuting /home/classes/cs223/Hwk10/test.Spellcheck
Public test script for Spellcheck (11/4/2020)
***** Checking for warning messages *****
Making -B ./Spellcheck
gcc -std=c99 -Wall -pedantic -g3 -c -o spellcheck.o spellcheck.c
gcc -std=c99 -Wall -pedantic -g3 -c -o dictionary.o dictionary.c
gcc -std=c99 -Wall -pedantic -g3 -c -o gmap.o gmap.c
gcc -std=c99 -Wall -pedantic -g3 -c -o char_key.o char_key.c
gcc -std=c99 -Wall -pedantic -g3 -o Spellcheck spellcheck.o dictionary.o gmap.o char_key.o
Each test is either passed or failed; there is no partial credit.
To execute the test labelled IJ, type one of the following commands
depending on whether the file /c/cs223/hw10/Tests/tIJ is executable or not
/c/cs223/hw10/Tests/tIJ
./Spellcheck < /c/cs223/hw10/Tests/tIJ
The answer expected is in /c/cs223/hw10/Tests/tIJ.out.
Dictionary Building
PASSED 001. Add 5 words with unique roots
PASSED 002. Add 5 words with the same first letter
PASSED 003. Add 15 words with the same four first letters
PASSED 004. Add 15 words that differ by one intermediate character at the same location
PASSED 005. Add a word with a prefix that already exists
PASSED 006. Digits, hyphens
Dictionary Building: 6 of 6 tests passed
Spellcheck
PASSED 007. Add 5 words with unique roots
PASSED 008. Add 5 words with the same first letter
PASSED 009. Add 15 words with the same four first letters
PASSED 010. Add 15 words that differ by one intermediate character at the same location
PASSED 011. Add a word with a prefix that already exists
Spellcheck: 5 of 5 tests passed
Valgrind
PASSED 012. Add 5 words with unique roots
PASSED 013. Add 15 words with the same four first letters
Valgrind: 2 of 2 tests passed
Deductions for Violating Specification (0 => no violation)
End of Public Script
13 of 13 Total tests passed for Spellcheck
Possible Deductions (assessed later as appropriate)
-10 Deficient style (comments, identifiers, formatting, ...)
-5 Does not make
-5 Makefile missing
-5 Makefile incorrect
-5 Log file incorrectly named
-5 Log file lacks estimated time
-5 Log file lacks total time
-5 Log file lacks statement of major difficulties
***** Checking log file *****
Estimate: ESTIMATE 1:00
Total: TOTAL 1:00
***** Checking makefile *****