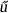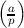 = 1 if a is a quadratic residue modulo p, -1
if a is a quadratic non-residue modulo p, and 0 if p∣a. Fact:
= 1 if a is a quadratic residue modulo p, -1
if a is a quadratic non-residue modulo p, and 0 if p∣a. Fact: 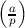 = a(p-1)∕2.
= a(p-1)∕2.
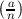 = ∏
i=1k
= ∏
i=1k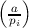 ei. (By convention, this product is 1 when k = 0, so
ei. (By convention, this product is 1 when k = 0, so 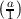 = 1.) The
Jacobi and Legendre symbols agree when n is an odd prime. If
= 1.) The
Jacobi and Legendre symbols agree when n is an odd prime. If 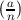 = -1 then a is definitely
not a quadratic residue modulo n, but if
= -1 then a is definitely
not a quadratic residue modulo n, but if 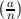 = 1, a might or might not be a quadratic residue.
= 1, a might or might not be a quadratic residue.
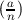 can be computed efficiently by a straightforward recursive
algorithm, based on the following identities:
can be computed efficiently by a straightforward recursive
algorithm, based on the following identities: 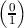 = 1;
= 1; 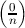 = 0 for n≠1;
= 0 for n≠1; 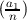 =
= 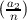 if a1 ≡ a2 (mod n);
if a1 ≡ a2 (mod n); 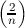 = 1 if n ≡ ±1 (mod 8);
= 1 if n ≡ ±1 (mod 8); 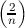 = -1 if n ≡ ±3 (mod 8);
= -1 if n ≡ ±3 (mod 8);
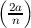 =
= 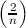
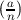 ;
; 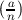 =
= 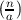 if a ≡ 1 (mod 4) or n ≡ 1 (mod 4);
if a ≡ 1 (mod 4) or n ≡ 1 (mod 4); 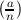 = -
= -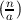 if
a ≡ n ≡ 3 (mod 4).
if
a ≡ n ≡ 3 (mod 4).
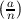 ⁄≡ a(n-1)∕2 (mod n). If n is prime, then for every a ∈ Z*n,
⁄≡ a(n-1)∕2 (mod n). If n is prime, then for every a ∈ Z*n,
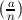 ≡ a(n-1)∕2 (mod n).
≡ a(n-1)∕2 (mod n).